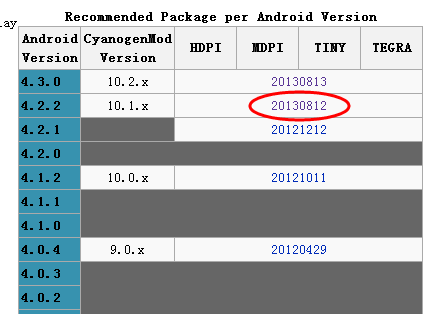
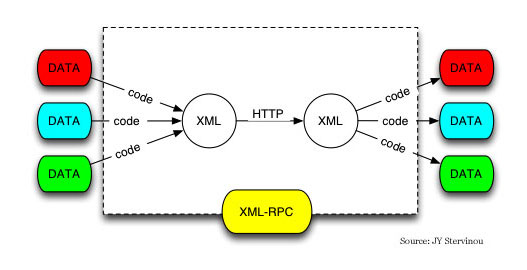
Overview(简介)
XML-RPC is a Remote Procedure Calling protocol that works over the Internet.
An XML-RPC message is an HTTP-POST request. The body of the request is in XML. A procedure executes on the server and the value it returns is also formatted in XML.
Procedure parameters can be scalars, numbers, strings, dates, etc.; and can also be complex record and list structures.
工作机制:
Request example(请求示例)
POST /RPC2 HTTP/1.0
User-Agent: Frontier/5.1.2 (WinNT)
Host: betty.userland.com
Content-Type: text/xml
Content-length: 181
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<methodCall>
<methodName>examples.getStateName</methodName>
<params>
<param>
<value><i4>41</i4></value>
</param>
</params>
</methodCall>
Header requirements(请求中需设置header的必要信息)
The format of the URI in the first line of the header is not specified. For example, it could be empty, a single slash, if the server is only handling XML-RPC calls. However, if the server is handling a mix of incoming HTTP requests, we allow the URI to help route the request to the code that handles XML-RPC requests. (In the example, the URI is /RPC2, telling the server to route the request to the "RPC2" responder.)
- A User-Agent and Host must be specified.
- The Content-Type is text/xml.
- The Content-Length must be specified and must be correct.
Payload format(请求的数据格式)
The payload is in XML, a single <methodCall> structure.
The <methodCall> must contain a <methodName> sub-item, a string, containing the name of the method to be called. The string may only contain identifier characters, upper and lower-case A-Z, the numeric characters, 0-9, underscore, dot, colon and slash. It's entirely up to the server to decide how to interpret the characters in a methodName.
For example, the methodName could be the name of a file containing a script that executes on an incoming request. It could be the name of a cell in a database table. Or it could be a path to a file contained within a hierarchy of folders and files.
If the procedure call has parameters, the <methodCall> must contain a <params> sub-item. The <params> sub-item can contain any number of <param>s, each of which has a <value>.
Scalar <value>s (基本数据类型)
<value>s can be scalars, type is indicated by nesting the value inside one of the tags listed in this table:
| Tag | Type | Example |
| <i4> or <int> | four-byte signed integer | -12 |
| <boolean> | 0 (false) or 1 (true) | 1 |
| <string> | string | hello world |
| <double> | double-precision signed floating point number | -12.214 |
| <dateTime.iso8601> | date/time | 19980717T14:08:55 |
| <base64> | base64-encoded binary | eW91IGNhbid0IHJlYWQgdGhpcyE= |
If no type is indicated, the type is string.
<struct>s (结构体类型)
A value can also be of type <struct>.
A <struct> contains <member>s and each <member> contains a <name> and a <value>.
Here's an example of a two-element <struct>:
<struct>
<member>
<name>lowerBound</name>
<value><i4>18</i4></value>
</member>
<member>
<name>upperBound</name>
<value><i4>139</i4></value>
</member>
</struct>
<struct>s can be recursive, any <value> may contain a <struct> or any other type, including an <array>, described below.
<array>s (数组类型)
A value can also be of type <array>.
An <array> contains a single <data> element, which can contain any number of <value>s.
Here's an example of a four-element array:
<array>
<data>
<value><i4>12</i4></value>
<value><string>Egypt</string></value>
<value><boolean>0</boolean></value>
<value><i4>-31</i4></value>
</data>
</array>
<array> elements do not have names.
You can mix types as the example above illustrates.
<arrays>s can be recursive, any value may contain an <array> or any other type, including a <struct>, described above.
Response example (回复示例)
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Connection: close
Content-Length: 158
Content-Type: text/xml
Date: Fri, 17 Jul 1998 19:55:08 GMT
Server: UserLand Frontier/5.1.2-WinNT
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<methodResponse>
<params>
<param>
<value><string>South Dakota</string></value>
</param>
</params>
</methodResponse>
Response format (回复的数据格式)
Unless there's a lower-level error, always return 200 OK.
The Content-Type is text/xml. Content-Length must be present and correct.
The body of the response is a single XML structure, a <methodResponse>, which can contain a single <params> which contains a single <param> which contains a single <value>.
The <methodResponse> could also contain a <fault> which contains a <value> which is a <struct> containing two elements, one named <faultCode>, an <int> and one named <faultString>, a <string>.
A <methodResponse> can not contain both a <fault> and a <params>.
Fault example (请求出错时的回复示例)
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Connection: close
Content-Length: 426
Content-Type: text/xml
Date: Fri, 17 Jul 1998 19:55:02 GMT
Server: UserLand Frontier/5.1.2-WinNT
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<methodResponse>
<fault>
<value>
<struct>
<member>
<name>faultCode</name>
<value><int>4</int></value>
</member>
<member>
<name>faultString</name>
<value><string>Too many parameters.</string></value>
</member>
</struct>
</value>
</fault>
</methodResponse>
官方spec: http://www.xmlrpc.com/spec